Today, more organizations face security threats that cause serious harm. Just look at the figures. A staggering 53% of companies have experienced a data breach related to third parties. An alarming 83% of companies also experienced a data breach more than once.
One thing is clear: Companies mustn’t only be concerned about business growth. They should also take the necessary steps to ensure the protection of their and their customers’ sensitive data. Otherwise, they face financial losses in the millions and reputational damage.
Conducting a security audit is an effective way to ensure this data protection. But what is a security audit? How do you conduct one?
Here’s a step-by-step guide for your business.
What is a security audit?
A security audit is a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s security infrastructure, policies, and procedures. The audit covers network configurations, access controls, data encryption methods, and physical security measures. It typically also involves testing to detect vulnerabilities in your system.
Overall, this process helps organizations improve their overall security posture.
Why should businesses prioritize regular security audits?
Regular security audits essentially help businesses address vulnerabilities in their systems and networks. As a result, companies can stay ahead of potential cyber threats and ensure the safety of sensitive data.
In addition, security audits provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of existing security measures and help businesses make informed decisions on these security strategies. They also assist companies when it comes to complying with industry regulations and standards. Regular assessments of security systems can help companies identify gaps or non-compliance issues so they can take the necessary actions and meet the requirements.
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) services are paramount for safeguarding businesses online against emerging quantum threats. Offering robust encryption methods resistant to quantum attacks, PQC ensures data integrity and confidentiality, fortifying businesses against evolving cyber risks in the digital landscape.
Furthermore, regular security audits can help companies build trust and, therefore, long-term relationships with customers. By demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information, businesses can establish a reputation as an organization worth transacting with.
Lastly, as I mentioned earlier, prioritizing regular security audits can save companies from costly data breaches and reputational damage in the long run. In 2022, the average cost of a data breach amounted to $4.35 million, 2.6% more than the $4.24 million reported in 2021. A whopping 46% of companies also reported experiencing damage to their brand value after a cyber security breach. You don’t want your company to be part of that statistic.
How frequently should security audits be undertaken?
The frequency of security audits is determined by several factors. This includes the industry in which the business operates, the sensitivity of the data being handled, and any specific regulations or standards that apply to the company.
For example, in industries like healthcare or finance where the risk of data breaches is higher, security audits may need to be conducted more frequently, perhaps monthly or quarterly. However, for businesses in less regulated industries, an annual audit or one held twice a year may be sufficient.
Ultimately, the goal should be to strike a balance between maintaining a robust security posture and avoiding unnecessary disruption to business operations.
4 essential steps for conducting a security audit
Now that we’ve answered the question “What is a security audit,” here are steps businesses should follow to conduct one.
Step 1: Planning
Planning for a security audit involves many tasks.
First, businesses should determine their main goals for the audit. Do you want to primarily assess your compliance to existing regulations? Or maybe your main goal is to upgrade your entire data security strategy? These goals serve as a road map for the audit process. You’ll want to determine your specific criteria for success as well.
Establishing the scope of the audit is just as important. The scope defines the boundaries and focus of the audit. You may need to identify the systems, networks, or processes you want to evaluate depending on the goals you established.
In the initial phase, you’ll also need to determine which team of experts will help you with the audit. Will you be hiring from outside the organization or will you rely on your existing tech professionals? Whatever you decide to do, you’ll need individuals with top security certifications in areas such as network professional security and Microsoft security. These certifications are proof of their knowledge and skills in their respective fields. Look for different individuals who excel in different security fields to ensure a well-rounded team capable of addressing all aspects of the audit.
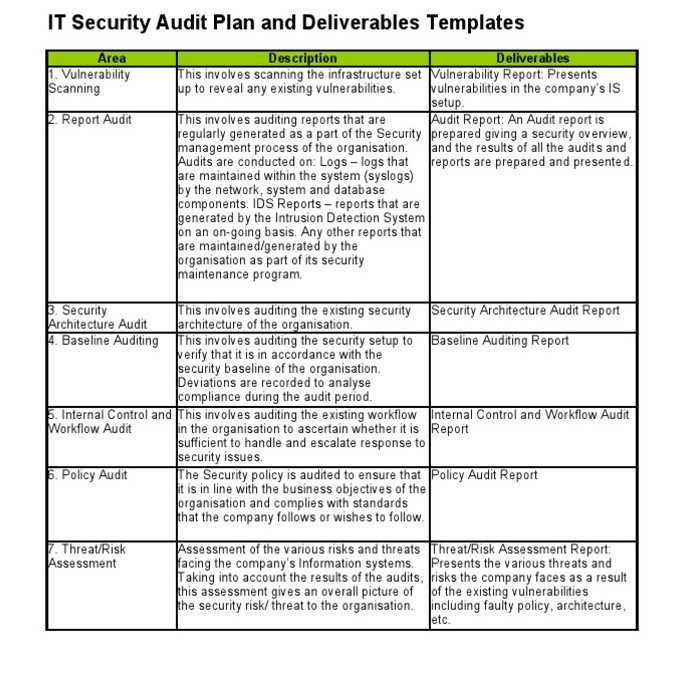
Once you have the above information, create a detailed audit plan. This plan should also outline the activities and timelines required for the audit. It should also include the methodologies and tools you’ll use. Additionally, regular reviews of eCommerce platforms could highlight the impact of disputes on retail health, providing insights comparable to those found in statistics that underline rising costs for merchants due to chargeback incidents. Here’s a plan you can use as a template:
Step 2: Preparation of documentation and others
Before your tech personnel can implement your security plan, all the necessary documentation and information need to be prepared. That includes the company’s current security policies and procedures, network diagrams, system configurations, and other relevant documentation that can provide insight into the organization’s security practices.
It is also crucial to gather information about any recent security incidents or breaches to identify potential areas of concern during the audit process. Ensure those in charge of the audit are updated with the latest industry standards and regulatory requirements. You can collate relevant resources for this so they can review them.
As part of the preparation pre-audit, interviews with key personnel, including IT administrators and executives, need to be conducted as well. This will help ensure those tasked with the audit have a holistic view of the company’s security protocols. With these interviews, they can also determine whether there’s a cybersecurity learning gap that needs to be addressed.
Step 3: Implementation and Testing
At this stage, all you and your tech personnel need to do is implement your security audit plan. Seek out the tech personnel you determined would conduct the systems testing properly. Brief them on the goals of the security audit and your planned security audit scope. Tell them how long the security audit should be. Provide them with the tech stack they need for their task, as specified during the planning stage as well.
Once your security team has everything they need, they can now start testing. Testing is a crucial step for organizations to evaluate their incident response plans and handle potential threats.
Your company can use several testing techniques.
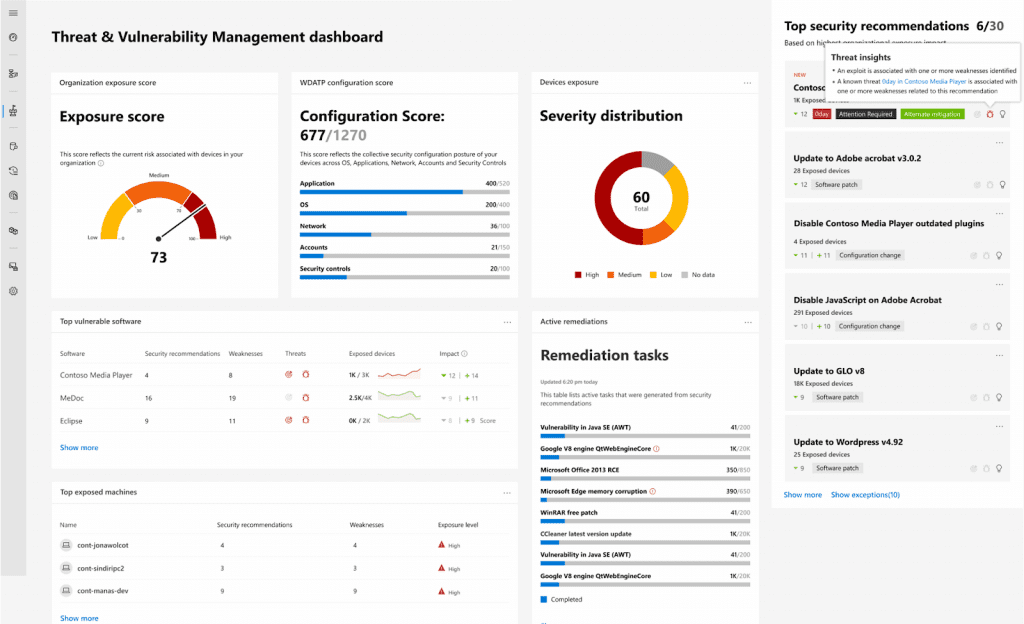
One method is to conduct a comprehensive scan of your applications, networks, and systems to identify potential vulnerabilities. This can be done using specialized tools and software like Wiz, Tenable Nessus, and Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management. The scan will help businesses identify outdated programs, flawed settings, and open ports, among others.
The tools also provide organizations with a detailed list of security areas they need to focus on. See below a report from Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management:
With this technique, businesses can get valuable insights into the potential consequences of a successful attack. Additionally, pentesting tools can be used for the management to allocate resources properly and prioritize risk mitigation efforts accordingly.
For the best results, it’s best to implement both techniques during an audit process.
Step 4: Reporting
Reporting should be part of any security audit. It ensures transparency within the organization, allowing stakeholders to understand the potential security risks. It also boosts security management since it helps ensure the allocation of resources where needed for the implementation of the necessary security measures.
Moreover, audit findings can serve as valuable documentation tools, providing a benchmark for future audits and facilitating the continuous improvement of security practices.
When reporting a security audit, key factors need to be considered. The assigned tech personnel should provide a clear and concise summary of the audit findings, highlighting any significant vulnerabilities or risks identified. For each possible point of vulnerability or risk, they should highlight the severity and likelihood of exploitation.
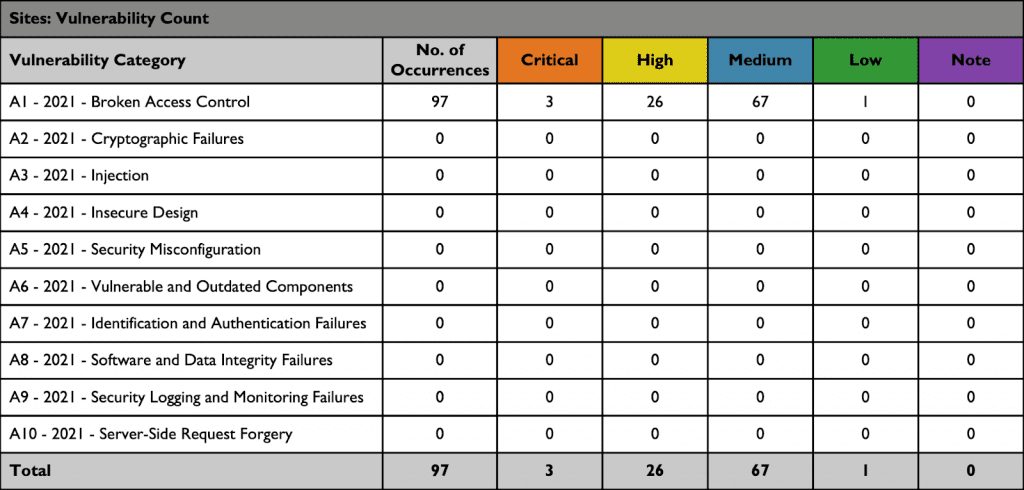
Here is a sample of a security audit that details the severity of each vulnerability category:
Both stakeholders with and without technical backgrounds should be able to readily grasp this summary.
Detailed information about the methodology and tools used during the audit process and any limitations that may have affected the audit’s scope should also be included. The personnel in charge of the report should also outline specific recommendations for addressing identified vulnerabilities or potential risks. These may include the implementation of security controls, patches, or updates. The personnel may even come up with something as specific as an AI policy template to ensure the risk of exposure to hackers of proprietary data learned by the company tool is mitigated.
Lastly, supporting evidence or documentation should be incorporated into the report. These may include log files or screenshots that validate the findings and enhance the report’s credibility.
With a comprehensive and easy-to-understand security audit report, businesses can effectively make decisions to improve the company’s overall security posture.
Conclusion
What is a security audit? It’s essentially a comprehensive evaluation of your company’s security infrastructure and policies. A comprehensive and proactive approach to security audits is critical to a company’s long-term success. With regular audits, the company can safeguard and protect sensitive information, not just of the business but also of its customers.
Create a detailed security audit plan and prepare the necessary documentation. Then the relevant personnel just need to implement the plan. Reporting should also be part of the security audit. The recommendations in the report can help inform decision-making.
With a thorough audit, you can have confidence in your organization’s ability to maintain a secure environment.