Logistics is a complex process that involves the movement of goods from one place to another.
Whether it’s a small package or a large shipment, keeping track of the items throughout the process is crucial to ensuring they arrive at their intended destination on time and in good condition.
Without accurate records and effective tracking systems, logistics would be a headache for everyone involved.
Various documents including purchase receipts, proof of shipment, proof of delivery, and shipping invoices help us keep track of shipped orders and confirm deliveries.
This article will discuss the various types, uses, and optimal strategies to create shipping invoices. It should help your company simplify the shipping paperwork, minimize the chance of rookie mistakes, and avoid unhappy customers.
What Is A Bill Of Lading?
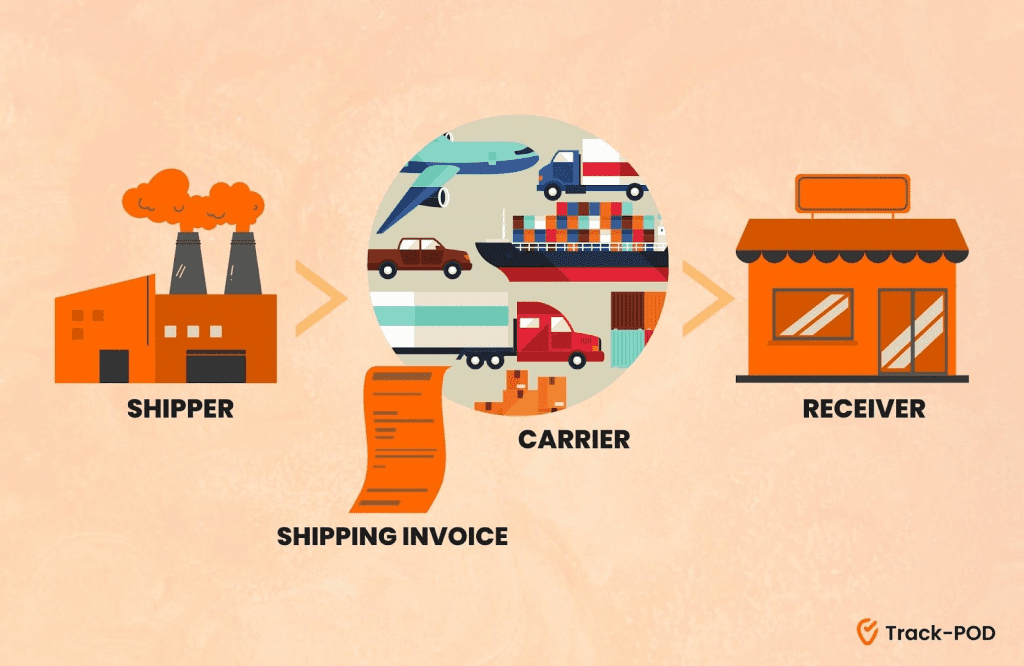
A bill of lading is a legal document that serves as evidence of a contract of carriage between a shipper and a carrier. It is a receipt for goods that have been shipped and a document of title that represents ownership of the goods. A bill of lading is typically used in the context of international trade, but it can also be used in domestic transportation.
Here is an example of how a bill of lading works:
Suppose that a company in New York wants to ship a container of goods to a customer in London. The company contracts with a shipping company to transport the container from the port in New York to the port in London. The shipping company issues a bill of lading to the company in New York, which serves as proof that the container has been received for shipment and sets out the terms of the contract of carriage.
The bill of lading includes information such as the name and address of the shipper and the carrier, a description of the goods being shipped, the destination port, and the freight charges. The bill of lading is signed by the carrier or its agent, acknowledging that the goods have been received for shipment.
When the container arrives at the port in London, the customer can obtain possession of the goods by presenting the original bill of lading to the carrier. The carrier will then release the goods to the customer, who becomes the owner of the goods.
In addition to serving as evidence of the contract of carriage and as a document of title, a bill of lading can also be used as a negotiable instrument. This means that the bill of lading can be endorsed and transferred to another party, who can then obtain possession of the goods. This can be useful in situations where the original consignee (the customer in our example) wants to sell the goods to another party before they arrive at the destination port.
Purpose Of A Shipping Invoice
The purpose of a shipping invoice is to provide information about the shipment, including the type and quantity of goods being shipped, their value, and any associated charges such as shipping and handling fees or taxes.
1. Receipt of names, physical characteristics, and condition of the shipped goods
The primary purpose of a shipping invoice is to list the items that were dispatched so that the right goods are sent and received. A business can provide specific names, physical characteristics, serial numbers, and other information needed to identify goods.
Companies sometimes list the goods’ condition to make sure that items are delivered in the same state.
The carrier issues a bill to the shipper in exchange for the shipment. It proves that the carrier received the shipment in good condition from the shipper company.
2. Statement of quantity, weight, measure, or number of packages
In addition to the standard physical and technical characteristics, the shipping invoice should also provide the quantity of each item type shipped. It can also include additional details, such as the total number of parcels and their combined weight and dimensions.
Shipping invoices can help the recipient quickly verify that no packages get lost in transit and that nothing is damaged.
Labeling the cargo can also help with customs clearance and compliance with regulations.
3. Proof of ownership for the listed goods
Both the sender and the carrier should make sure that the invoice is properly filled out with accurate ownership information.
Each party, including the shipper, carrier, and recipient, must be mentioned on a bill of lading. This way, if the cargo is misplaced, the rightful owner can be determined quickly.
Using the bill of lading, the recipient can easily contact the seller for any issues concerning returns, exchanges, or other legal matters.
4. Legal contract between the carrier and the shipper (owner)
According to UNCTAD’s definition, a shipping invoice can outline the terms and conditions of the goods transportation. It acts as a legal contract that can include the responsibilities of both parties, the type and condition of the cargo, and the delivery schedule.
Disclaimer: if you are shipping something, then you’ll require an e-Way Bill too! (Don’t know what e-way bills are? Learn Everything To Know About e-Way Bills) Check out this comprehensive list of Top e-Way Bill Software

What Needs To Be Included On A Bill Of Lading?
A bill of lading is an important document in the transportation of goods by sea, land, or air. The following information should be included on a bill of lading:
- Date of Issue: The date on which the bill of lading is issued should be clearly stated.
- Shipper’s Name and Address: The name and address of the company or individual who is shipping the goods should be listed on the bill of lading.
- Consignee’s Name and Address: The name and address of the company or individual who is receiving the goods should also be listed.
- Carrier’s Name and Address: The name and address of the company or individual who is transporting the goods should be stated.
- Description of Goods: A detailed description of the goods being transported should be included on the bill of lading, including the type, quantity, weight, and dimensions of the goods.
- Number of Packages: The number of packages being shipped should be stated, along with any identifying marks or numbers on the packages.
- Freight Charges: The amount of money that the shipper has agreed to pay for the transportation of the goods should be included.
- Shipping Terms: The terms of the shipment should be listed, including the place of origin, the destination, and any specific instructions for delivery.
- Signature of Carrier: The bill of lading should be signed by the carrier or its authorized agent, indicating that the goods have been received for shipment.
It is important to ensure that all of the information on the bill of lading is accurate and complete, as errors or omissions can cause delays or other problems with the shipment.
Recommended Reads: Top 7 Invoice Generator Software
Shipping Invoice Types And Use Cases
Shipping invoices can be categorized based on the type of goods shipped, the transportation method, the number of carriers, and the delivery location. These details determine the type of shipping invoice needed for a business.
We’ll look more closely at the most common types of bills of lading and their use cases.
– Negotiable vs. non-negotiable bill of lading
A negotiable shipping invoice, as outlined by the Corporate Finance Institute, acknowledges the cargo owner’s rights to the goods and allows the shipper to transfer ownership under certain conditions. A bill of lading contract, in other words, may be transferred to a third party. This invoice form is also known as a ‘to order’ bill of lading.
Open bill of lading is a common term for the negotiable type of invoice that permits the shipment to be transferred to another recepient.
The recepient is often a third-party retailer selling items on the manufacturer’s behalf. In contrast to a non-negotiable bill of lading, it is a negotiable document.
Shipments of items that have already been paid for (donations, presents) are typically accompanied by a non-negotiable or straight bill of lading. In that case, there is no need to change legal cargo owners since payment for the shipment is made in advance.
As a non-negotiable invoice, a bearer bill of lading is used when delivery is to be made to the recipient holding the bill of lading (the “Bearer”).
– Clean vs. claused bill of lading
A clean BOL is issued after the carrier inspects packages for quality and quantity. Both the carrier and shipper sign this invoice when assured of the good’s quality. A clean bill of lading guarantees the goods were shipped without any damage or loss.
If the courier finds any broken or flawed items, the bill of lading is “claused” as the opposite of a “clean” invoice.
A claused bill of lading is a document that a carrier provides if some goods are lost, stolen, or damaged before or during shipping.
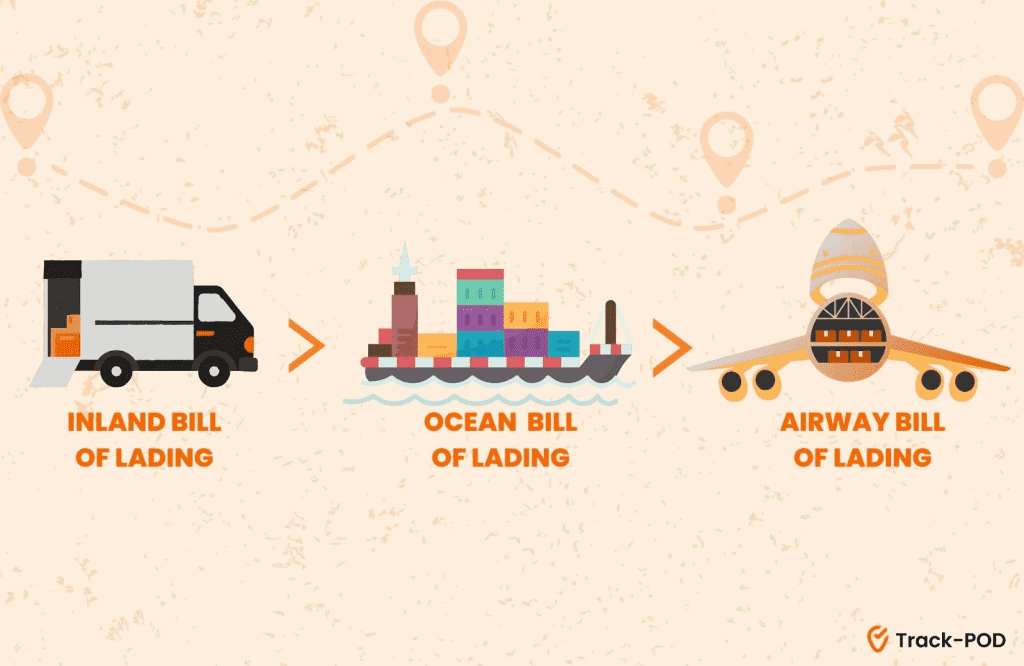
– Inland vs. ocean vs. airway bill of lading
When it comes to international shipping, we can specify three common types of invoices: inland, ocean, and airway. In other words, each shipment is documented with its own bill of lading for each part of the journey.
An inland bill of lading is an invoice that escorts the cargo if it travels by land before it goes by sea or air. The inland bill of lading covers the ground transportation part of the cargo’s journey.
An ocean bill of lading is needed when a shipment goes through international waters. If the same vessel is used to deliver the cargo, then a carrier presents a direct bill of lading.
Carriers that ship goods by air distribute airway bills of lading, similarly to ocean bills of lading.
– Master bill of lading vs. house bill of lading
A House Bill Of Lading (HBL) is a document used by buyers and sellers of goods to prove their shipment. A freight forwarder usually issues it to the customers involved. Simply put, it is a direct contract between the cargo shipper and the carrier company.
A Master Bill of Lading (MBL) has a different purpose than an HBL. The carrier issues it for use between the NVOCC (Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier) and freight forwarders in domestic and international locations.
In other words, it is a contract between the carriers/freight forwarders that states how the goods will be moved.
A single MBL can include information about more than one shipment. It is used to send packages from different places/senders to the same destination. In this scenario, the MBL lists each shipment’s contents and individual bill of lading numbers. Most of the time, master bills of lading are used for ocean and multi-carrier shipping.
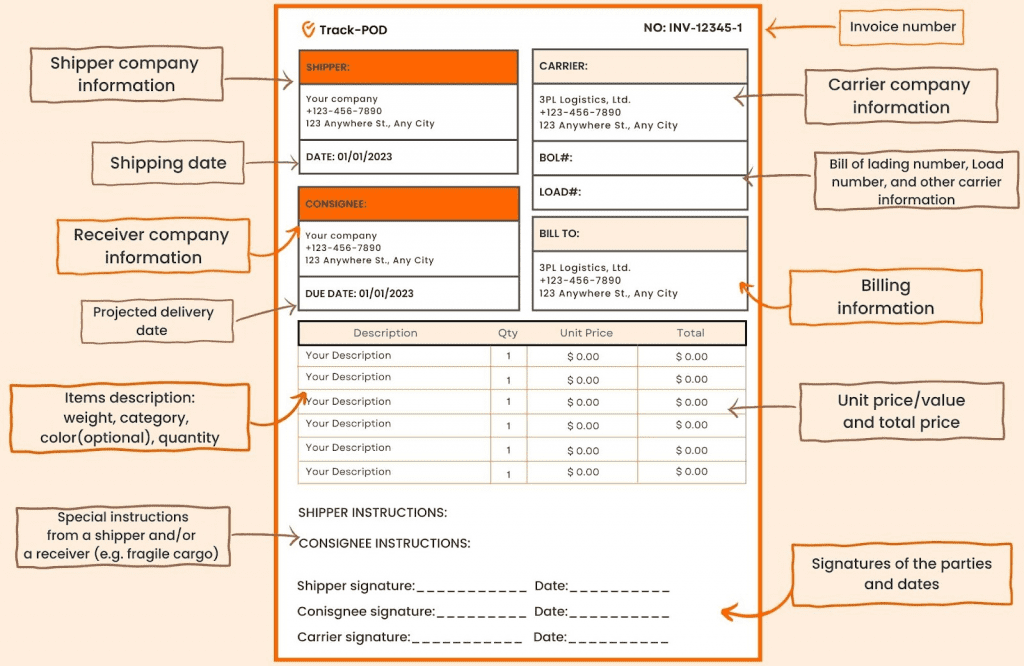
Shipping Invoice Components And Best Practices
Even though each type of shipping invoice can have some extra information and fields, the shipping invoice will all have the same basic structure.
Let’s look at the standard components of a shipping invoice and some best practices for creating them.
1. Shipper’s and recipients information
Ownership information helps avoid mistakes in the delivery process. The bill of lading should include the following information for both the shipper and the consignee (recipient):
- Full name/company name/company legal number
- Full address
- Contact phone number, business email address
2. Shipping date and delivery date
Those help determine when the shipment left the shipper’s facility and when it should arrive at its destination.
3. Bill of lading number
Includes load number, tracking number, and other information provided by the carrier to identify the cargo.
4. Billing information
Billing nformation refers to the information about a company or person who will pay or already paid for the shipment. It can be the consignee or a third party.
It features the amount to be paid, along with information about freight charges status (pre-paid, to be paid, etc.).
5. Shipment item description
Labelling the packages ensures that the right goods reach their intended destination. The item description should include:
- Names, serial numbers
- Quantity of each item type
- Weight, color, measure (optional)
- Unit value and total price
6. Special instructions provided by the shipper, carrier, or consignee
This field is used when the carrier is dealing with cargo that is fragile, expensive, or needs to be kept at a certain temperature.
7. All parties’ signatures with dates
Shipper, carrier, and consignee should all sign a shipping invoice to confirm the successful delivery of goods.
How To Create A Bill Of Lading
Numerous online tools are available to assist your company in creating and customizing your bill of lading.
You can save time and effort by using one of the many automated invoice processing tools to organize your client and carrier information.
Depending on the type of invoice, one method is to download a free shipping invoice template. Bill of lading templates for Excel and Word are simple to edit and print.
Another option is to use online tools, such as Refrens Invoice Generator, Microsoft Build tool, Shopify constructor, or any available top invoicing software, to print a bill of lading.
Wrapping Up
Shipping invoices are crucial documents for logistical operations. They are used to ensure the shipment is successfully and legally delivered to the recipient.
You can select the type of invoice that best suits your business needs based on the cargo’s nature, transportation mode, and delivery location. To create and customize your bill of lading, you can use multiple invoice creation guides and templates available for free or with a paid subscription.
It is important to ensure that the shipping invoice accurately reflects the goods being transported and their value, as this can affect customs duties and taxes. Additionally, including clear payment terms and instructions can help avoid payment delays or disputes.
To streamline this process further, consider using invoice and packing list software. Such software can help you efficiently manage and customize your shipping documents, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
We hope you find this guide helpful in creating, printing, and customizing shipping invoices for your business.