Have you recently come across the trendy term “gig economy” used by many individuals? But, like most of them, are you confused about what it means?
As the world prepares for mid-2022, amid the fear of the COVID-19 variation ‘Omicron,’ there is great optimism for both employees and employers on the horizon. According to the most recent research, the gig economy will be the primary source of new jobs.
We sought to get answers through this research, which will explain the phrase “gig economy” and how you might participate in it and contribute to the future.
Over and above, the workforce, workspace, and work platforms are all undergoing a paradigm shift in the workplace. The geographical boundaries of work are blurring every day, thanks to next-generation technology and new-age workers.
Millennials and gen Z workers are discovering long-term work options in the world’s rapidly increasing gig economy as these individuals do not want to be limited by a schedule.
Additionally, the global pandemic untied work from the office and ushered in a new industry known as the “Gig Economy.”
A gig economy is an economic activity in which employees are hired on a temporary, contractual, or freelance basis to complete specific tasks or projects.
It includes all platforms that hire freelancers, consultants, and gig workers from various fields such as IT, digital marketing, communication, food and beverage, content development, and art and design. As a result, a gig economy entails an organization using temporary or part-time professionals rather than full-time employees.
From The Lens Of Stats
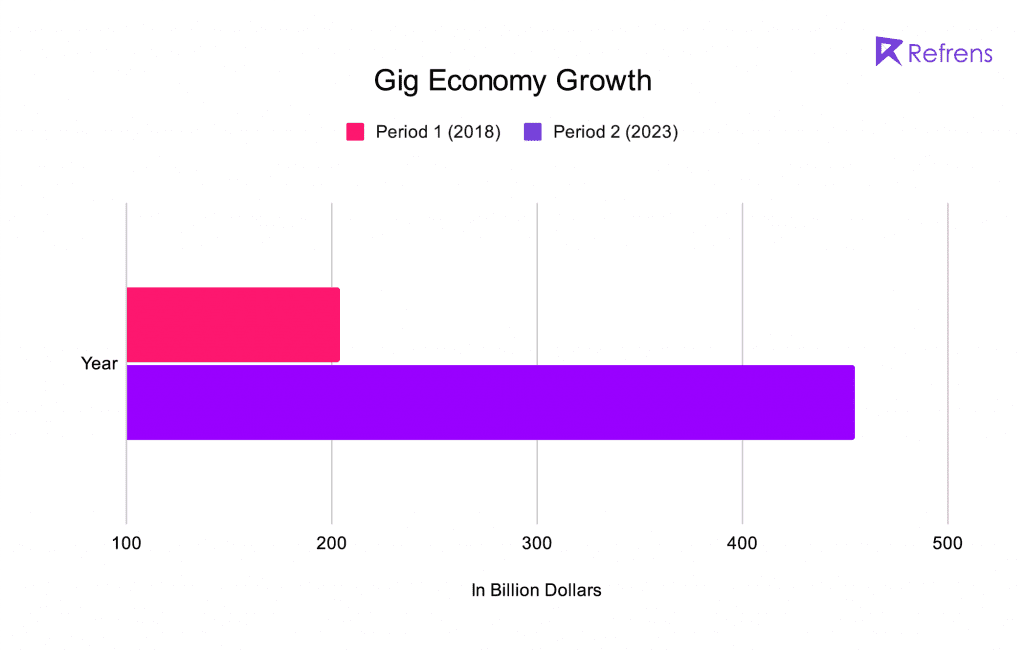
- As per the grab below, the global gig economy is anticipated to increase from $204 billion in 2018 to $455 billion in 2023, representing a 17.4% compound annual growth rate.
- There was also a subsequent rise in the number of freelance employees. Let’s take an instance of freelancers in the United States, which is expected to increase from 57 million to 86 million by 2027. The UK’s gig economy workforce more than doubled from 2016 to 2019, totalling 4.7 million workers.
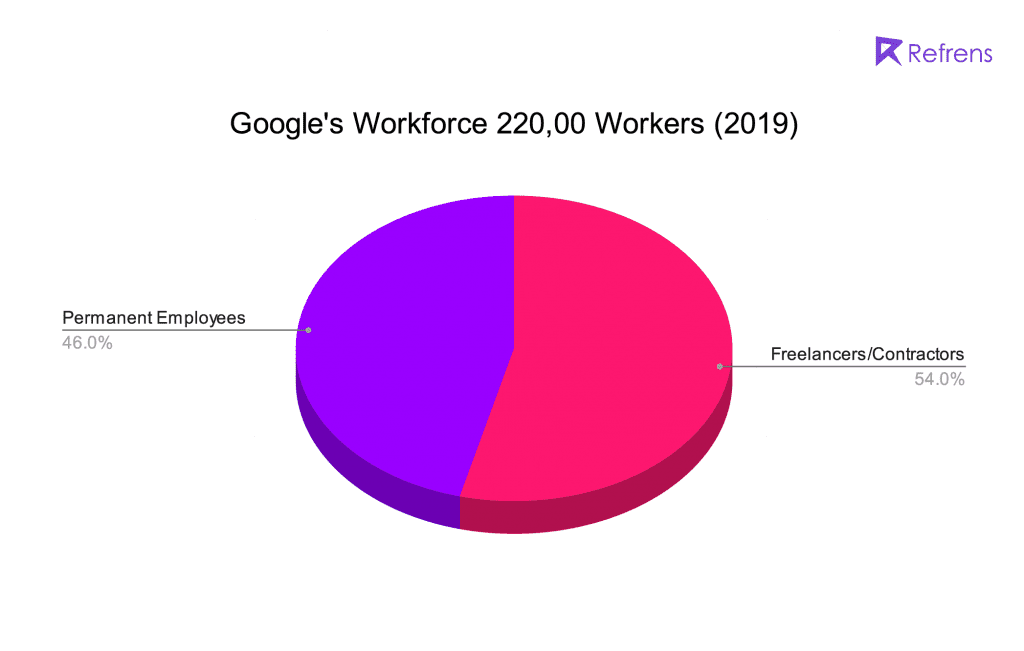
- As per the Pie chart below it’s quite visible that: there are more freelancers than permanent workers at Google. Google has 120,000 contractors/freelancers on its payroll as of March 2019, which was higher than the 102,000 regular employees on the payroll.
- Additionally, the gig economy is expected to grow to $455 billion in India in 2024, almost two times the pre covid estimates.
These estimates from the most significant economies give us a big idea about how the gig economy is the world’s future.
Freelancing is the most visible form of the gig economy. The gig economy has been able to thrive because of the Internet and big data, which has allowed it to expand into services that people can utilize. To negotiate a trade or complete a transaction nowadays, all you need is access to the Internet.
- These freelancers charge an average hourly rate of $21 around the world.
- Moreover, the number of high-earning freelancers with an annual income of $100,000 or more continues to rise year after year.
What Role Does Gig Economy Play In The Future Of Employment?
Gone are the days when freelancers had to invest a significant amount of time in developing their professional reputations before earning their first dollar. These days, the digital platforms that underpin the gig economy take care of this.
These platforms remove barriers to entry into significant areas of the economy by providing precise consumer assessment tools, simple dispute resolution procedures, and rigorous verification processes.
Thanks to the new wave of online platforms like Refrens, these gig workers who participate in short-term “digital employment” or “gigs” can receive money after each assignment.
The success of freelancing demonstrates that the gig economy is viable and appropriate for the future of work. Many businesses believe that hiring freelancers with specific expertise is a better long-term approach for keeping up with changing market demands than permanent retraining personnel.
Over and above, no one can afford to sit on their couches in this age of technological advancement. Market demands are constantly changing due to rapid technological improvement. The technology makes traditional professional climb considerably more challenging, particularly for freelancers. Their achievements on one platform are often not recognized by another if they do not follow a planned professional path – but it does help them maintain their abilities up to date.
International communication has become more affordable because of Slack and Google Meet tools. Thousands of free, world-class courses are now available on websites that anybody may access from prestigious universities. Thousands of articles and megabytes of data are available at the touch of a button.
As a result, the gig economy may soon be identified with highly-skilled, self-employed employees rather than the comparably low-skilled occupations of the service industry.
Factors That Drive Gig Economy

- The rise of startup culture
Recruiting full-time staff is expensive for fledgling entrepreneurs new to the startup environment. Businesses prefer to recruit freelancers based on customer tasks and specifications to maximize resource efficiency. The rise of startup culture is a boon for millennials looking to get into the gig economy.
Check out this post on when to hire a freelancer Vs a full-time employee to save money.
- Millennials attitude towards work
With the development of globalization and digital invasion, millennials are taking a more progressive attitude to employment. Workplace stress and demanding schedules in the private sector have recently altered millennials’ perceptions. Growth prospects, a regular flow of jobs, a better work-life balance, and flexibility are all factors that attract young talent to leave the corporate work culture for freelancing.
- Generation X is looking for work
Freelancing isn’t just for millennials anymore; Gen X is also getting into it. They benefit from incentives such as flexible work hours, flexibility to maintain work-life balance, a consultative approach, and a dream for their career speciality and new-age profiles as they gradually transition to freelance after earning the necessary job experience.
- Contract-based labour by MNCs
The more prominent market players are gradually hiring young talent on a contract basis for small businesses. MNCs use Flexi-hiring to cut costs, save time, and effectively manage operational expenses and time, giving new and aspiring talent tremendous opportunity and exposure. According to the EY survey, 20 percent of companies with more than 1,000 employees have a 30 percent or more contingent workforce.
- Freelancing platform growth
The advent of freelancing platforms has fueled the gig economy’s growth in the United States and worldwide. Many domestic and international media link companies and freelancers worldwide, allowing businesses to outsource labor at a low cost and freelancers to make a living on their terms.
- Payments based on blockchain
Last but not least, payment mode is viewed as one of the challenges for freelancers. According to a recent survey conducted, freelancers are optimistic about their prospects; nonetheless, most believe their main difficulty is inconsistent revenue. However, the introduction of the blockchain-based payment system has sped up the financial transaction process, resulting in greater transparency in the payment structure.
Check out the best international payment gateway.
How Can Businesses Adapt The Changing Work?
Let’s dive into how businesses can use these factors in their organization.
When hiring gig workers for the first time, businesses may face difficulties. They’ll have to think about a lot of things. To begin with, several countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom, have been involved in continuing legal challenges over the classification of gig workers. The treatment of gig workers in terms of benefits, company insurance, and taxation are among the concerns being considered.
Companies that are ready to embark on a gig economy strategy should take the following actions to adjust and adapt to prepare for a gig workforce:
- Put in place policies that encourage flexibility.
- Create standard contracts and explicit standards for the gig and non-gig workers on their ability to do gig employment to ensure legal appropriateness.
- Think about a remuneration plan, perks, and other compensation for gig workers.
- Review the company’s talent acquisition requirements and essential traits when employing gig workers.
- Review the current recruiting structure to enable gigging, and implement processes and controls to track gigger performance.
- Enable technology skills, such as remote work policies and improved IT procedures for cybersecurity concerns.
- Look at “Resourcing” from a holistic viewpoint, complete with a flexible, sustainable, and inexpensive resourcing strategy for now and the future.
To ensure a successful and lasting gig economy strategy, you must be responsive to change, embrace change, recognize the necessity of top-down transformation, lead the strategic implementation of the “future perfect team,” and encourage your team’s growth.
As a result, MNCs will be able to adapt to the changing work climate and hire cost-effective gig workers.
Check out the 27 proven ways to align freelancer to your company’s goal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gig Workers
For freelancers:
The following are the key advantages of the gig economy for workers:
- Pay is dependent on performance rather than a yearly salary increase.
- Pick up and earn with a flexible work schedule.
- More Possibilities of work that are not reliant on location.
- A wide range of gig platforms in many industries is now available.
Aside from the advantages, there are also drawbacks:
- Traditional employment perks such as health insurance and paid time off are not available.
- Isolation and a lack of cultural affinity for a corporation.
For businesses,
The gig economy can also benefit employers:
- Cost savings as a result of new employment models that are more inventive.
- Recruitment, recruiting, and interviewing costs are all reduced.
- You’ll have access to a diverse pool of talent.
However, you should be aware of the following pitfalls:
- Some governments have strict contractor status restrictions.
- Employee loyalty to the company is dwindling.
The Journey Ahead : Is Gig Economy The Future Of Work ?
The world’s work culture is undergoing a symbolic transformation. The gig economy is increasing; with roaring technical changes, the continually altering nature of employment, and the global pandemic, it’s predicted to at least double.
The gig economy is being hailed as the new working-class standard, with an inflow of gig workers and freelancers anticipated to enter. The gig economy has the potential to transform the world of work as we know it, thanks to technological advancements and government regulations and initiatives.
Moreover, work satisfaction is becoming more important to millennials than any other statistic regarding finding the ideal employment. Hyper-connectivity, career security, and the fluid dynamics of engagement are all critical factors in considerably boosting the gig economy.
Also, regardless of whatever side of the ocean you are on, everyone is learning to cope with the gig economy, working a little too hard while dealing with the COVID. Our advice is to stay as updated as possible with technological advancements while not being burned out in the process. In addition to this, schedule time for rest, self-care, and relaxation to ensure you’re at the top of your freelancing game.
Recommended Reads: 15 Best Invoicing Software In 2024